

The formula will evaluate to 2, if the supplier_id is between 21 and 30. The formula will evaluate to 1, if the supplier_id is between 11 and 20. The formula will evaluate to 0, if the supplier_id is between 1 and 10. In this example, based on the formula: TRUNC ((supplier_id - 1) / 10 However, you can try to create a formula that will evaluate to one number for a given range, and another number for the next range, and so on.ĭECODE(TRUNC ((supplier_id - 1) / 10), 0, 'category 1', Question: I would like to know if it's possible to use the DECODE function for ranges of numbers, ie 1-10 = 'category 1', 11-20 = 'category 2', rather than having to individually decode each number.Īnswer: Unfortunately, you can not use the DECODE function for ranges of numbers. The date example above could be modified as follows: LEAST(date1, date2) Helpful Tip #2: One of our viewers suggested using the LEAST function (instead of the DECODE function) as follows: Sales Bonuses DECODE(SIGN(actual-target), -1, 'NO Bonus for you', 0,'Just made it', 1, 'Congrats, you are a winner') The SIGN/DECODE combination is also helpful for numeric comparisons e.g. The date example above could be modified as follows: DECODE(SIGN(date1-date2), 1, date2, date1) Helpful Tip #1: One of our viewers suggested combining the SIGN function with the DECODE function as follows: The formula below would equal 0, if date1 is greater than date2: (date1 - date2) - ABS(date1 - date2) Otherwise, the DECODE function should return date1.Īnswer: To accomplish this, use the DECODE function as follows: DECODE((date1 - date2) - ABS(date1 - date2), 0, date2, date1)
#SQL DECODE HOW TO#
This is because NUMERIC is the data type with the highest precedence that is compatible with both.Question: One of our viewers wanted to know how to use the DECODE function to compare two dates (ie: date1 and date2), where if date1 > date2, the DECODE function should return date2. For example, if result is an integer and default is a fractional number, DECODE returns a value with data type NUMERIC. If the data types of result and default are different, the data type returned is the type most compatible with all of the possible return values, the data type with the highest data type precedence. For numeric values, DECODE returns the largest length, precision, and scale from all of the possible result argument values. If the data type of the first result argument cannot be determined, DECODE returns VARCHAR. Data Type of Returned ValueĭECODE returns the data type of the first result argument. Note that DECODE is supported for Oracle compatibility.
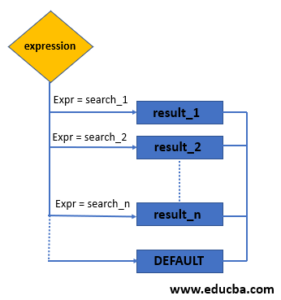
If expr is null, InterSystems IRIS returns the result of the first search that is also null. In a DECODE expression, InterSystems IRIS considers two nulls to be equivalent. Therefore, InterSystems IRIS never evaluates a search if a previous search is equal to expr.
InterSystems IRIS evaluates each search value only before comparing it to expr, rather than evaluating all search values before comparing any of them to expr. If expr is not equal to any search value, the default value is returned, or, if default is omitted, null is returned. If expr is equal to a search value, the corresponding result is returned. To evaluate a DECODE expression, InterSystems IRIS compares expr to each search value, one by one:

The search, result, and default values can be derived from expressions. The maximum number of parameters in the DECODE expression (including expr, search, result, and default) is about 100. You can specify multiple search, result pairs, separated by commas. Optional - The default value which is returned if expr does not match any search. The value which is returned if expr matches search.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
